K8s Security | Authorization
Why Authorization?
在 K8s 中,不同類型的實體(例如 Admins、Developers、Bots)執行的操作權限應有所區隔,以維護叢集的安全性與資源隔離。因此,我們需要使用 授權機制(Authorization Mechanisms) 來精細控管誰可以做什麼。
Authorization Mechanisms
Node Authorizer
Node Authorizer 是一種專門授權給 Kubernetes kubelet(節點代理程式) 的機制,允許它只能存取與其自身相關的資源。
這是一種特殊的授權方式,僅適用於節點自身,與一般使用者授權不同。
📌 補充:kubelet 還能讀取其所在節點的 ConfigMap 和 Secrets(如果 pod 有 mount)。
- 認證方式:
Kube API Server通過 user identity 與 TLS certificate 判斷請求來源是否為節點。
- 適用對象:
kubelet(節點)
- 節點允許操作的資源範圍如下:
- Read: Services、Endpoints、Nodes(僅限自身資訊)、Pods(僅限指派給該 Node 的 Pods)
- Write: Node status、Pod status、events
ABAC
ABAC 是早期 Kubernetes 所支援的授權機制之一,透過靜態 JSON policy 檔案控制每個使用者對資源的操作權限。
- 缺點:
- 無法細緻管理
- 權限定義採靜態設定,不易維護
- 無法動態調整:無法根據動態條件做出授權決策
- 無法做到角色抽象(Role-based grouping)
- 設定變更需重新啟動 API Server
- 實務現況:
- 已被 RBAC 取代,Kubernetes 1.8+ 預設啟用 RBAC。
ABAC 實例說明
| 使用者 / 群組 | 權限內容 |
|---|---|
dev-user |
可檢視、建立、刪除 Pods |
dev-user-2 |
可檢視、建立、刪除 Pods |
dev-users |
(群組)可檢視、建立、刪除 Pods |
security-1 |
可檢視與核准 CSR(憑證簽署請求) |
完整 ABAC Policy(單一使用者範例)(e.g. dev-user)
1 | { |
多筆簡化 ABAC Policy(陣列格式)
1 | [ |
RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)
RBAC 是目前 Kubernetes 預設且推薦使用的授權機制,透過角色與綁定來控制使用者與資源間的權限關係。
- 設計理念
- Role/ClusterRole:定義一組權限(verbs + resources)
- RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding:將角色賦予給特定的使用者、群組或 ServiceAccount
權限範例角色設計
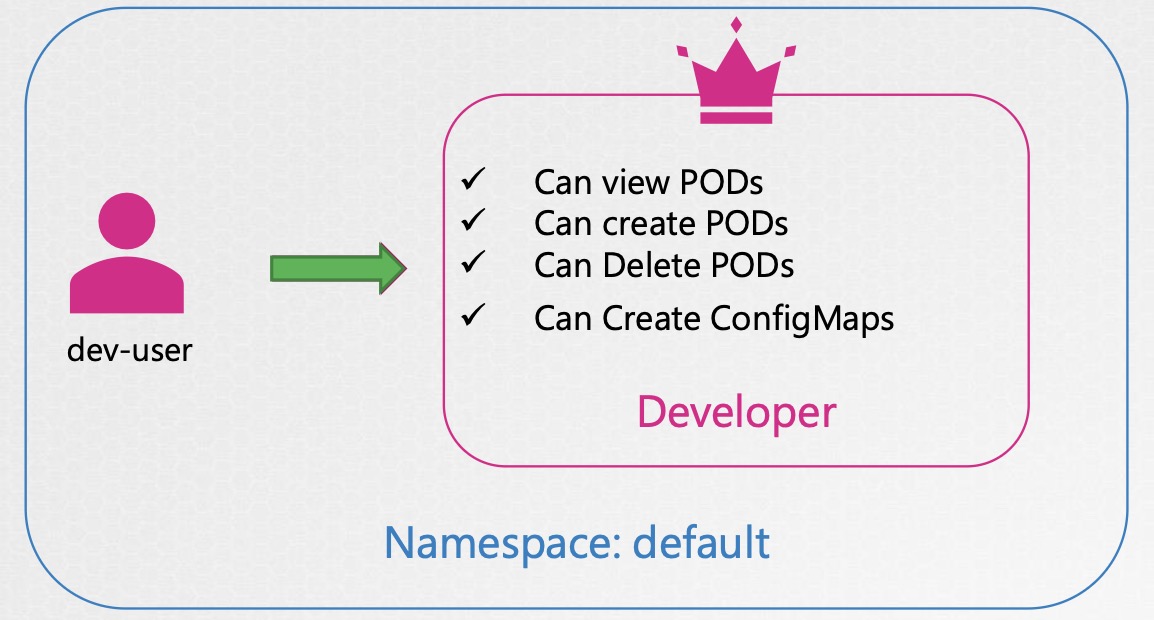
- Developer 角色
- ✓ Can view PODs
- ✓ Can create PODs
- ✓ Can Delete PODs
- ✓ Can Create ConfigMaps
- 對應使用者/群組:dev-user, dev-user-2, dev-users
- Security 角色
- ✓ Can view CSR(CertificateSigningRequest, 憑證簽署流程資源)
- ✓ Can approve CSR
- 對應使用者: security-1
Webhook (OPA)
Webhook 模式允許 K8s 把授權判斷交由外部系統決策,最常見的實作是 OPA - Open Policy Agent。
Gatekeeper是實作 OPA 的常用工具。
授權流程
- 使用者(例如
dev-user)發送操作請求,例如建立 Pod。 - API Server 傳送請求至 OPA webhook:API Server 根據 –authorization-mode=Webhook 設定,呼叫外部 Webhook 伺服器。
- Webhook(如 OPA)根據 Rego Policy 檢查是否允許(allow)該操作。
- Webhook 回傳 JSON 結果:
- HTTP 200 OK
allowed: true(或 false)1
2
3
4
5
6
7{
"apiVersion": "authorization.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "SubjectAccessReview",
"status": {
"allowed": true
}
}
Authorization Mode(授權模式)
Kubernetes 支援多種授權模式,可同時啟用、並依照順序判斷:
| 模式類型 | 說明 |
|---|---|
Node |
僅授權 kubelet 對自己相關資源進行操作 |
ABAC |
靜態 JSON-based 授權(已不建議) |
RBAC |
推薦使用的角色型授權,支援群組、角色綁定等 |
Webhook |
呼叫外部系統(如 OPA)進行決策 |
AlwaysAllow |
所有請求都允許(不安全,僅用於測試) |
AlwaysDeny |
所有請求都拒絕(不實用) |
API Server 啟動參數範例
1 | ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kube-apiserver \ |
可同時啟用多種授權機制,系統會依序進行授權檢查。
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC,Webhook 的授權順序如下:**Node → RBAC → Webhook**
一旦任一授權模式允許該請求,API Server 即允許此操作。
⚠ ABAC 與 RBAC 無法同時混用,需在啟動參數中選擇要用哪一個,且 ABAC 修改 policy 後需重啟 API Server。
RBAC
API Group 與 RBAC 對應關係
| 資源 | API Group | RBAC 設定 |
|---|---|---|
| pods | "" (core group) |
apiGroups: [""] |
| deployments | apps (apps group) |
apiGroups: ["apps"] |
| RBAC 相關資源(roles, rolebindings) | rbac.authorization.k8s.io |
apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"] |
Role 定義範例
- Role 是 namespace 級別的權限設定。
- developer role 允許對 pods 做常用操作,並可建立 configmaps。
- 可限制特定資源名稱(resourceNames)來細化權限。
RoleBinding 綁定使用者
- RoleBinding 將 Role 角色授權給特定 user 或 group。
- 可綁定 User、Group 兩種 kind,方便配合 AD/LDAP 使用。
補充:Role/RoleBinding vs ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding
| 角色類型 | 使用範圍 | 適用場景 |
|---|---|---|
| Role/RoleBinding | 單一 namespace | 需限制在某 namespace |
| ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding | 全 cluster 或跨 namespace | 跨 namespace 或需存取 cluster-wide 資源如 nodes、secrets |
⚠ 補充:「若你需讓一個 ServiceAccount 存取不同 namespace 的資源,應使用 ClusterRole + RoleBinding 在各命名空間分別綁定」。
補充:ClusterRoleBinding
- 將 ClusterRole 授權給特定使用者,作用範圍為整個 cluster 或跨 namespace。
實務場景應用建議
| 用途 | 建議方式 |
|---|---|
| 單 Namespace 權限控制 | 使用 Role + RoleBinding |
| 跨 Namespace 或叢集資源 | 使用 ClusterRole + ClusterRoleBinding |
| 外部政策控制 | 整合 OPA + Gatekeeper |
| 動態用戶群管理 | 搭配 AD/LDAP group |
指令操作
Create Role

developer-role.yaml
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 |
developer-role.yaml 補充:Resource Names
developer-role.yaml 補充:Resource Names限制只能使用哪些 resourceNames (“blue”, “orange”)
1 | # developer-role.yaml |
Kubectl Command
1 | kubectl create -f developer-role.yaml |
Binding role and users
developer-role.yaml
同上
devuser-developer-binding.yaml
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 |
RBAC 的 subjects 支援 3 種 kind
RBAC 的 subjects 支援 3 種 kind:
1 | subjects: |
📌 當你的 cluster 使用 AD/LDAP 整合,group 綁定會非常常見。
Kubectl Command
1 | kubectl create -f devuser-developer-binding.yaml |
常用指令
View RBAC
查看角色與綁定
1 | kubectl get roles |
針對角色詳細資訊
1 | kubectl describe role [role_name] |
Check Access
權限檢查
1 | kubectl auth can-i [verb] [resource] --as [user] --namespace [ns] |
若是 ClusterRole,記得補上 --all-namespaces 或 --namespace 以驗證生效範圍。
1 | kubectl auth can-i get pods --as dev-user --namespace default |
小結
- Kubernetes 提供多種授權模式:
- Node Authorizer:授權 kubelet 等 node 元件存取必要資源
- ABAC:透過靜態 JSON Policy 授權(已較少使用)
- RBAC:最常見,透過 Role/ClusterRole 與 RoleBinding 控管權限
- Webhook:交由外部系統如 OPA 決策授權
--authorization-mode可同時啟用多種授權機制(Node, RBAC, Webhook)- RBAC 基本結構:
Role/ClusterRole定義權限RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding指派權限給 User/Group/ServiceAccount
- 開發常用工具:
kubectl auth can-ikubectl get roles、rolebindingskubectl describe role快速 debug 權限
📌 下一步建議:
了解 ServiceAccount 與 RoleBinding 搭配 Pod 運行身份,進入實務應用場景。

