Kubernetes | Deployment
Deployment
An API object that manages a replicated application, typically by running Pods with no local state.
📌 A Kubernetes Deployment is a higher-level object that provides capabilities such as seamless rolling updates to underlying instances, the ability to undo changes, and the option to pause and resume changes as required.
📌 Kubernetes Deployments are commonly used to deploy and manage multiple instances of applications in a production environment.
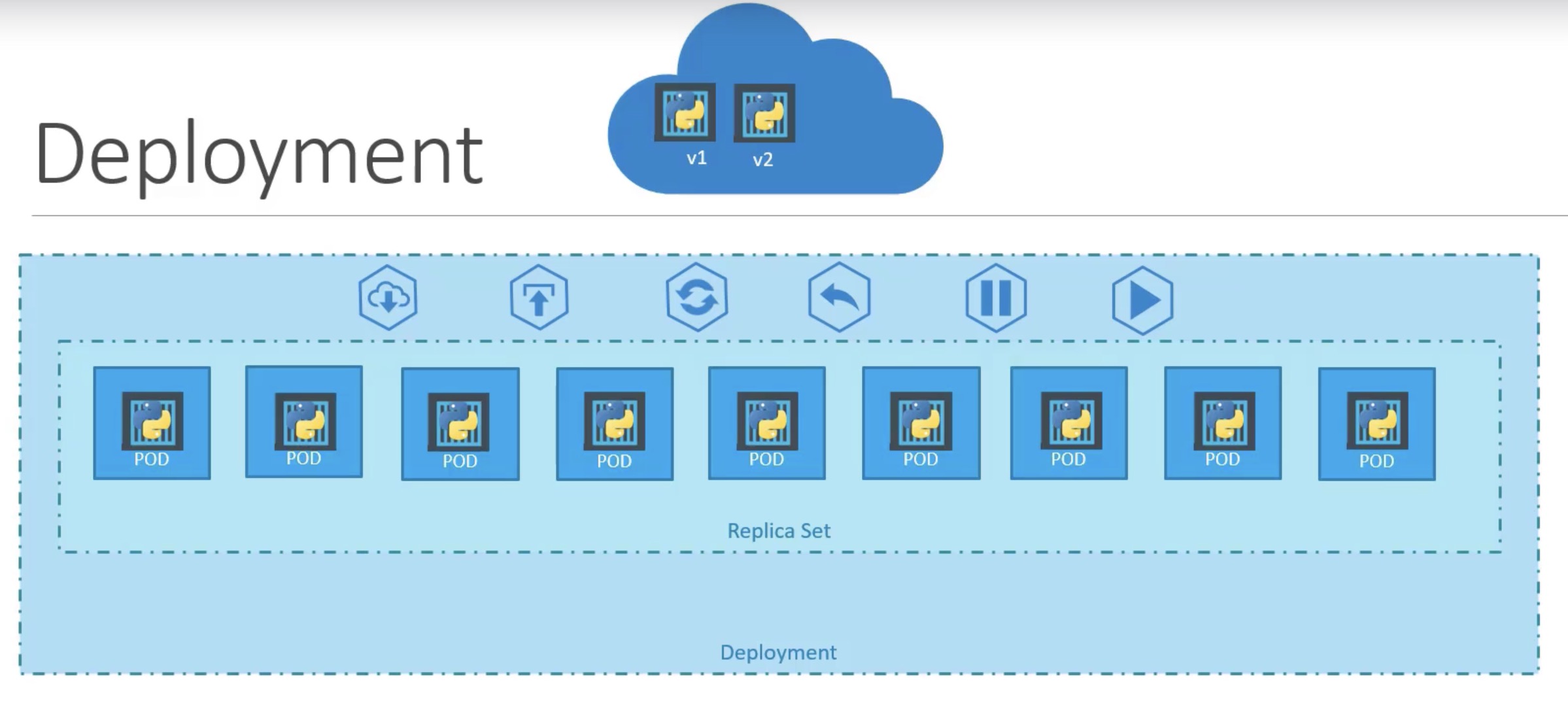
Key Reasons for Using a Deployment
Rolling Updates:- This allows for seamless updates to the underlying instances (pods) without downtime by gradually replacing the old versions of pods with new ones.
Don't upgrade all at once, as it may impact users accessing your applications. Instead, upgrade one after the other, using a process called rolling updates.
Rollback:- If something goes wrong during an update, a Deployment can undo changes and revert to a previous stable state.
- Undo the recent change. Roll back the changes that were recently carried out.
Pause and Resume:- Updates can be paused and resumed, which is useful for controlling the deployment process and debugging issues.
- You don’t want to apply each change immediately after the command is run. Instead, you would like to apply a pause to your environment, make the changes, and then resume so that all the changes are rolled out together.
Deployment with YAML
Template:
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1 |
deployment-definition.yml
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1 |
RUN commands
1 | kubectl create -f deployment-definition.yml |

1 | kubectl get all |

👍 Quickly create Kubernetes YAML Templates
In k8s version 1.19+, we can specify the –replicas option to create a deployment with 3 replicas.
1 | kubectl create deployment --image=httpd:2.4-alpine httpd-frontend --replicas=3 |
kubectl create vs. kubectl run
📝 kubectl create
Create a resource from a file or from stdin.
JSON and YAML formats are accepted.
Create a deployment
1 | kubectl create deployment --image=nginx nginx |
Generate Deployment YAML file (-o yaml). Don’t create it(–dry-run) and save it to a file.
1 | kubectl create deployment --image=nginx nginx --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-deployment.yaml |
Make necessary changes to the file (for example, adding more replicas) and then create the deployment.
1 | kubectl create -f nginx-deployment.yaml |
📝 kubectl run
Create and run a particular image in a
pod.
Create an NGINX Pod
1 | kubectl run nginx --image=nginx |
Generate POD Manifest YAML file (-o yaml). Don’t create it (–dry-run) and save it to a file.
1 | kubectl run redis --image=redis --dry-run=client -o yaml > redis_template.yaml |
References

